Hand Safety First
Whip Stop – Whip Socks
Whip Stop – Whip Socks
Share




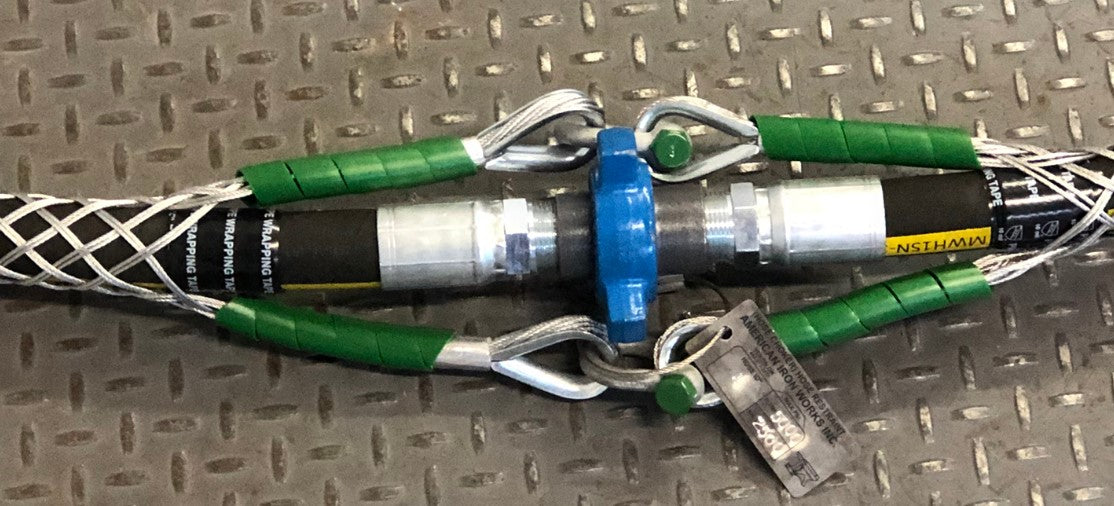


Whip Check
Introducing WHIP STOP
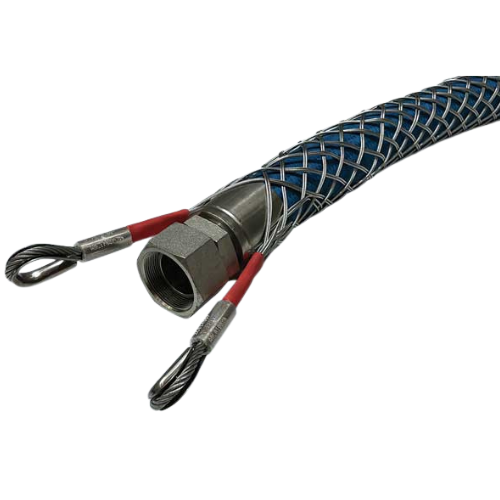
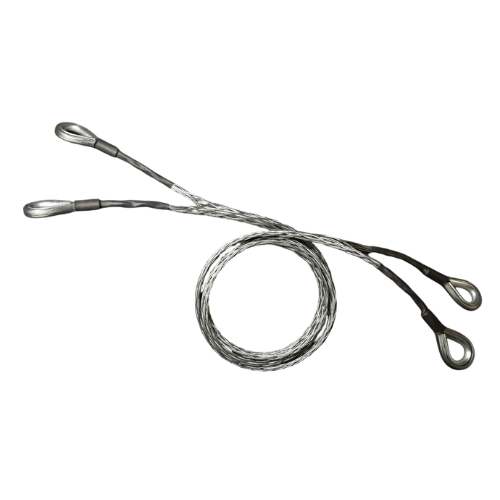
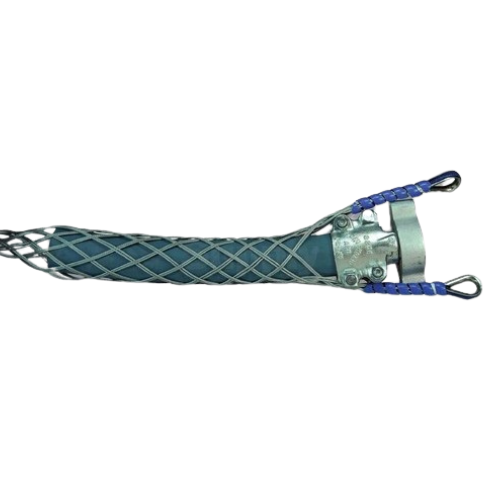
Recognized as one of the most effective high pressure hose restraint devices, Whip Socks are designed to prevent serious injury or death in the event of a hose breakage. Named for their construction, Whip Sock Hose Stops low-top style devices fit around the hose in a manner similar to a woven steel sock. The purpose is to provide a wider grip on the hose to secure it and prevent it from swinging around violently if the hose becomes dislodged during a high pressure accident.
Whip socks are high pressure hose safety restraint devices designed to prevent serious injury or death. The unique braided design reliably stops unpredictable and potentially dangerous movement of the high pressure hose. Used for a variety of high pressure pipes including air, water, hydraulic and mud. A new and better way to hold high pressure hoses.
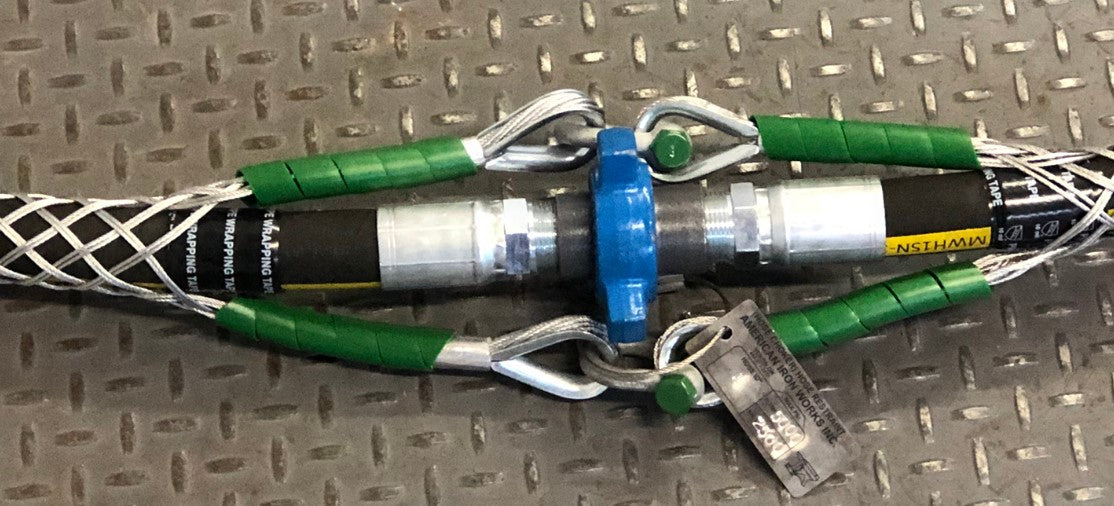
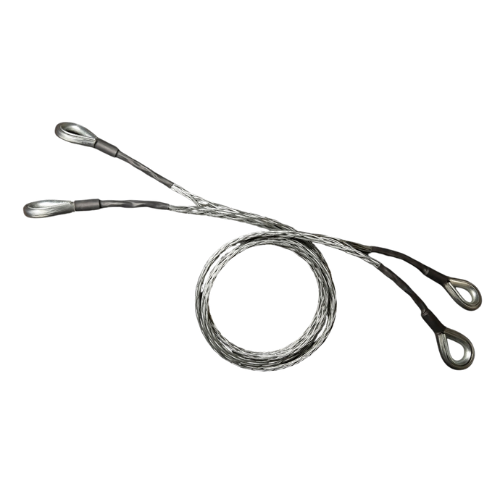
Benefits of Whip Stop – Whip Socks
There are several devices available to prevent hose sagging in case of an unexpected hose sagging incident. In order to protect the pipe from potential arrangements, it not only suppresses the organized cable restraint facility, but also prevents whiplash.
Our whip socks are used not only as air horses safety devices but also as other hoses. They can be incorporated into hose safety systems for a variety of applications where different substances are transferred via a high pressure pipe, including; Air, liquid, water, hydraulics, suspension, mud, etc.
The whip sock is made for safety as a main function. In the event of a refusal, there is a unique design that prevents high -pressure hoses unpredictable and potentially dangerous. As a result, the whipstop is perfect for all the jobs where the staff is working closely with high -pressure pipes.

Specification
Zinc plating steel or stainless steel alloy
Wicker
Sustainable
Universal application
Restaurants for exposure to chemical substances, impacts, and impact on ultraviolet rays
Can be used in various notes and pressure size
Show a double stop of a whisk

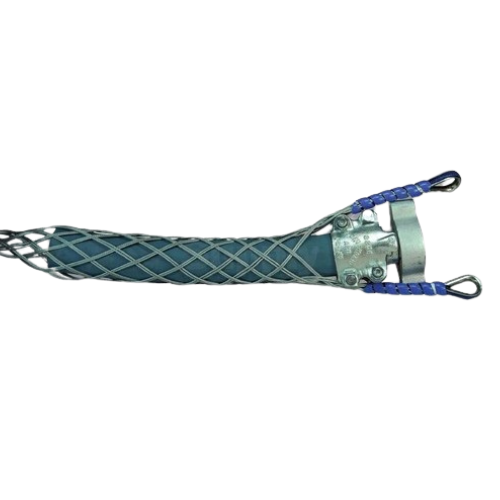
Function
The whipped cap is made of a Wicker steel cable that turns on a small pipe or pipe. The design is performed so that the force is generated from the inside, the cable is delayed on the pipe, and thus monitor the expansion of the pipe.This mechanism is effective in highlighting the main features: two fixing points and long grip area. We offer different pressure levels for application compatibility in both the anchor points and the shackles.Failure to comply with the pressure rating or using anchors and supports with a different pressure rating may result in system failure in the event of a rupture.

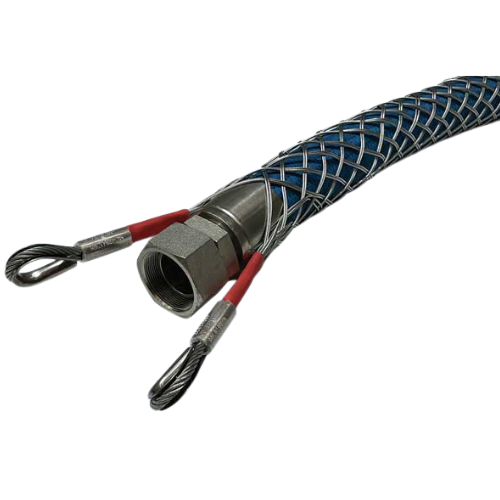
Installing a Sag Limiter
Ensure that the sag limiter fits securely to the pipe, install it carefully and level. After installing the pipe, make sure the mesh diamonds are the same width and length to ensure a tight fit. After installation, clamp the hose and pull the whip stop. It should not slip. If it does slip, it is too big and you should replace the whip stop with the correct size one. We recommend inspecting your Whip Stop periodically after installation. Ensure there are no stretched or torn terminals or broken wires. Be sure to check for rust on the whisk socket and any broken individual strands. This means that the speed limiter is overloaded and must be removed from service and replaced with a new one.
See the strength calculation table for more information on the rated capacity of the pipe and the impact of potential breakage.

Safety Precautions to Remember
Always assess your work before you begin and use personal protective equipment. Also, make sure all equipment has been tested before use.
Ensure all hoses, fittings, and safety devices are rated for the exact hose pressures
Double check joint connections, fittings, compressed air hose clamps and coupling matching
Only rely on premium quality safety equipment to safeguard your high pressure hoses; unreliable safety products can cause unfortunate results.
Keep your hoses free from contact with any corrosive chemicals, sharp objects, charged surfaces, etc.
Avoid increasing your dissatisfaction with the current pressure at all costs.
Train staff to study the potential dangers that exist and to use safety devices correctly.








